How to Use the Data Archiving Function
Route: FAQ - [ How to Use the Data Archiving Function ]Data used in DoingLabel (including imported data and editing configurations) is cached in the browser, and this type of data is called cached data. Cached data offers the highest storage efficiency and fastest access speed. However, it has a drawback: browser caches are exclusive, meaning cached data is not shared between different browsers.
To address this issue, DoingLabel previously provided the [Export Cache File] and [Import Cache File] functions. These functions allow you to export browser-cached data as a text file, which can then be copied to any computer and imported into the browser on that computer to transfer the cached data.

While this method enables data transfer between browsers, it relies on cache files as an intermediate medium—requiring copying, transferring, and importing the files, which is not very convenient.
Therefore, DoingLabel has developed the Data Archiving function. Archived data refers to cached browser data that is uploaded to DoingLabel’s servers for storage and backup. When needed, you can retrieve the archived data from the server and overwrite the local browser’s data. This eliminates the need for file-based intermediaries, allowing you to freely access and use the data anywhere with an internet connection.
It is important to note that archived data is stored in association with a license code. If multiple users share the same license code, all of them can operate on the archived data linked to that key.
For example: If User A and User B use the same license code, User B can access and use the archived data created by User A, and User A can delete the archived data created by User B.
How to Use the Data Archiving Function?
- Go to [License Code] and click [Upload & Retrieve Archive Data] button to open the Data Archiving function interface.

Apply archived data: In the [Apply] section, all archived data is listed.
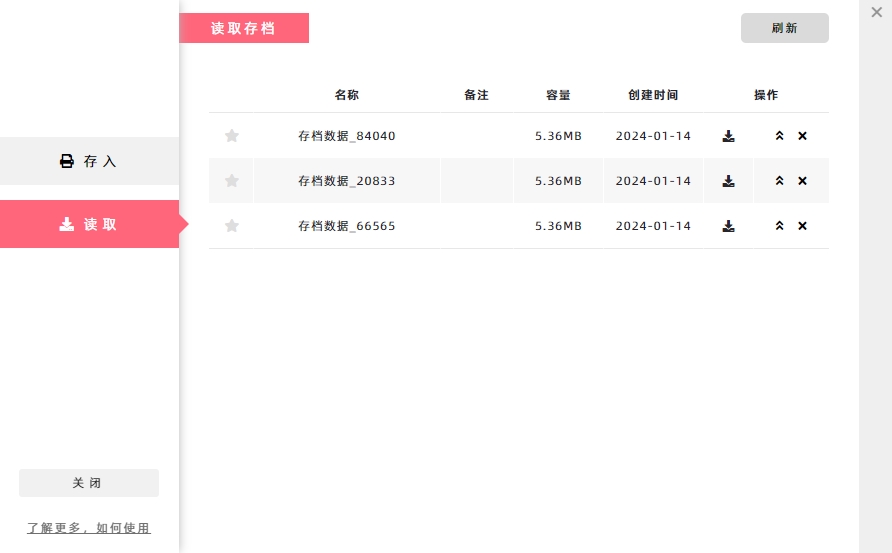
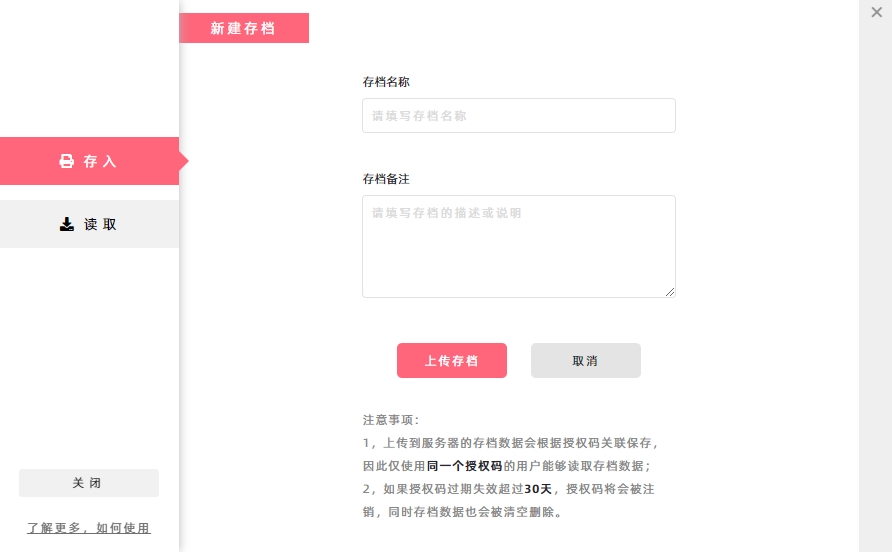
Upload data to archive: In the [Save] section, click [Upload Archive] button to package the local cached data and upload it to the remote server for storage.
- If you leave [Archive Name] blank, the system will automatically assign a default name.
- [Archive Remark] is a text description of the archive and can be left blank.
Scenarios for Using Data Archiving
1. Preventing Loss of Cached Data
Cached data is stored in the browser. Clearing the browser cache, uninstalling the browser, reinstalling the operating system, or replacing the computer will all lead to the loss of cached data. This is not an issue with archived data—since it is stored on remote servers, you can simply retrieve the archived data and overwrite the local browser’s data to restore it when switching to a new browser.
2. Sharing Cached Data Among Multiple Users
If you want to use cached data accumulated over a long period on another computer or share it with colleagues, you can use the Data Archiving function. As long as users share the same license code, they can access the archived data collectively.
3. Collaborative Workflows
For example: The marketing department has label data but no printer, while the printing department has a printer but no label data. The marketing department can edit the label data (which is saved as cached data), create an archive of it, and the printing department can then retrieve the corresponding archive, overwrite their local cache with it, and print the labels. This enables collaborative work between multiple users.
Learn more: [What Are Cached Data and Archived Data?]
- Kindly refrain from reposting this article unless you have obtained permission.
- This is a translated article. Should you find any translation mistakes or content errors, please refer to the Original Article (Chinese), which takes precedence.
- Due to ongoing version iterations, the feature details and interface screenshots included in this article may not be updated in a timely manner, leading to potential discrepancies between the article content and the actual product. For the most accurate information, please refer to the features of the latest version.